Gellary item number 1
Published:
FD-DeepLoc combined with DMO PSF engineering enables whole cell 3D super-resolution imaging over large FOV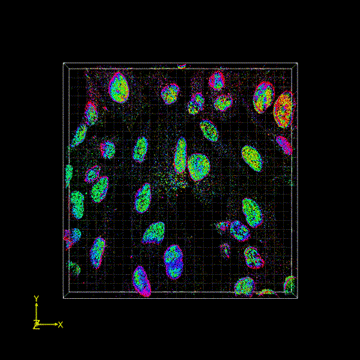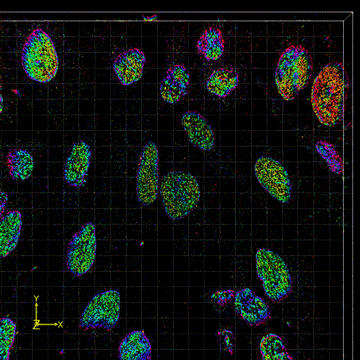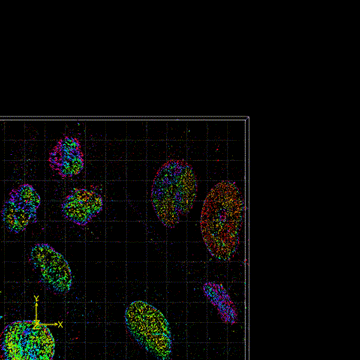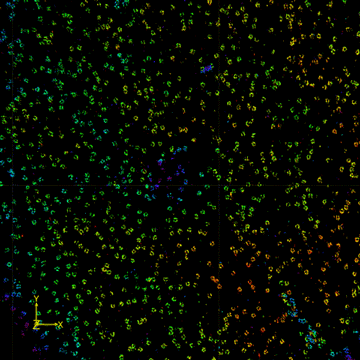
Published:
FD-DeepLoc combined with DMO PSF engineering enables whole cell 3D super-resolution imaging over large FOV
Published:
Short description of gellary item number 2 
Published:
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Published:
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
Published in Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2010
Published in ACS Nano, 2013
Published in Science Advances, 2015
Published in Nanoscale, 2016
Published in bioRxiv, 2017
Published in Nature Methods, 2018
Published in Biomedical Optics Express, 2019
Published in Nature Methods, 2019
Published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters, 2020
Published in Nature Methods, 2020
Published in Optics Letters, 2020
Published in Nature Protocols, 2021
Published in Engineering, 2022
Published in Optics Letters, 2022
Published in Optics Letters, 2022
Published in Journal of Cell Biology, 2022
Published in Nature Communications, 2022
Published in Nature Communication, 2022
Published in Chinese Optics, 2022
Published in Nature methods, 2023
Published in Clinical and Translational Medicine, 2023
Published in Optics Express, 2023
Published in Photonics Research, 2024
Published in CCS Chemistry, 2024
Published in Optics Letters, 2024
Published in Nature Methods, 2024
Published in Nature Methods, 2024
Published in Science Advances, 2024
Published in Nature communications, 2024
Published in Analytical Chemistry, 2024
Published in Optics Express, 2024
Published in nature cell biology, 2025
Published in Optics Letters , 2025
Published in Photonics Research, 2025
Published in Nature communications, 2025
Published:
fit3Dcspline is a GPU based 3D single molecule fitter for arbitrary, experimental point spread functions (PSF). The fitting speeds achieves more than 10^5 fits/s on a consumer graphic card GTX 1070. The implmentation of the fitting algorithm is based on maximum likelihood estimation and employs Levenberg-Marquardt optimization routine, which reaches theoretical minimum uncertainty. Both the EMCCD and sCMOS noise model are included. The softare package also includes tools to robustly model beads based experimental PSFs of different modality and correct for depth induce aberrations.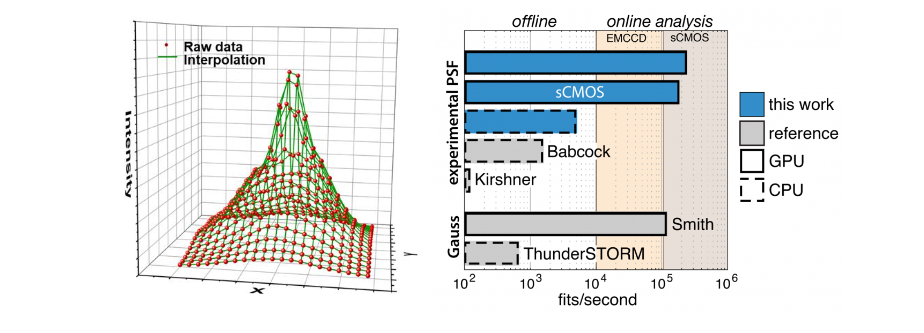
Published:
Ratiometric-4Pi is a graphics processing unit (GPU) based global fitting algorithm for 4Pi-SMLM with flexible PSF modeling and parameter sharing, to extract maximum information from 4Pi single molecule data and achieved both good color separation and optimal 3D resolution. By partially linking the photon parameters between channels with interference difference of π during global fitting of the multi-channel 4Pi single molecule data, we showed on simulated data that the loss of the localization precision is minimal compared with the theoretical minimum uncertainty, the Cramer-Rao lower bound (CRLB). Our algorithm is implemented in GPU and the fitting speeds is more than 38 times faster than the CPU based code.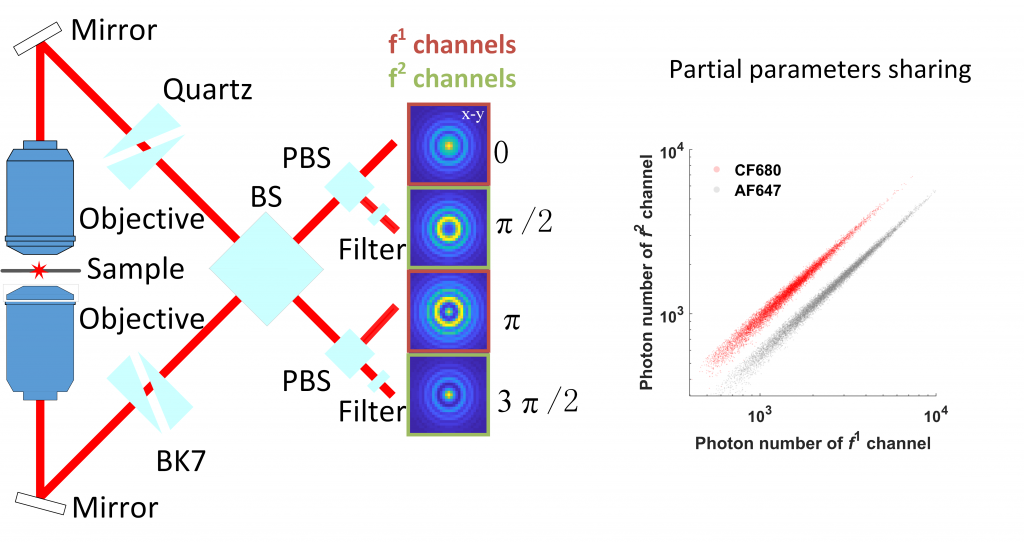
Published:
Point spread function (PSF) engineering is an important technique to encode the properties (e.g., 3D positions, color, and orientation) of a single molecule in the shape of the PSF, often with the help of a programmable phase modulator. A deformable mirror (DM) is currently the most widely used phase modulator for fluorescence detection as it shows negligible photon loss. However, it relies on careful calibration for precise wavefront control. Therefore, design of an optimal PSF not only relies on the theoretical calculation of the maximum information content, but also the physical behavior of the phase modulator, which is often ignored during the optimization process. Here, we develop a framework for PSF engineering which could generate a device specific optimal PSF for 3D super-resolution imaging using a DM. We use our method to generate two types of PSFs with depths of field comparable to the widely used astigmatism and tetrapod PSFs, respectively. We demonstrate the superior performance of the DM specific optimal PSF over the conventional astigmatism and tetrapod PSF both theoretically and experimentally.
Published:
GlobLoc is a graphics processing unit (GPU) based global fitting algorithm with flexible PSF modeling and parameter sharing, to extract maximum information from multi-channel single molecule data. Global fitting can substantially improve the 3D localization precision for biplane and 4Pi SMLM and color assignment for ratiometric multicolor imaging. The fitting speeds achieve ~35,000 fits/s on a standard GPU (NVIDIA RTX3090) for regions of interest (ROI) with a size of 13×13 pixels.
Published:
Field dependent deep learning enables high-throughput whole-cell 3D super-resolution imaging.Single-molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) in a typical wide-field setup has been widely used for investigating sub-cellular structures with super resolution. However, field-dependent aberrations restrict the field of view (FOV) to only few tens of micrometers. Here, we present a deep learning method for precise localization of spatially variant point emitters (FD-DeepLoc) over a large FOV covering the full chip of a modern sCMOS camera. Using a graphic processing unit (GPU) based vectorial PSF fitter, we can fast and accurately fit the spatially variant point spread function (PSF) of a high numerical aperture (NA) objective in the entire FOV. Combined with deformable mirror based optimal PSF engineering, we demonstrate high-accuracy 3D SMLM over a volume of ~180 × 180 × 5 μm3, allowing us to image mitochondria and nuclear pore complex in the entire cells in a single imaging cycle without hardware scanning - a 100-fold increase in throughput compared to the state-of-the-art.
Published:
The recent development of single molecule imaging techniques has enabled not only high accuracy spatial resolution imaging but also information rich functional imaging. Abundant information of the single molecules can be encoded in its diffraction pattern and be extracted precisely (e.g. 3D position, wavelength, dipole orientation). However, sophisticated high dimensional point spread function (PSF) modeling and analyzing methods have greatly impeded the broad accessibility of these techniques. Here, we present a graphics processing unit (GPU)-based B-spline PSF modeling method which could flexibly model high dimensional PSFs with arbitrary shape without greatly increasing the model parameters. Our B-spline fitter achieves 100 times speed improvement and minimal uncertainty for each dimension, enabling efficient high dimensional single molecule analysis. We demonstrated, both in simulations and experiments, the universality and flexibility of our B-spline fitter to accurately extract the abundant information from different types of high dimensional single molecule data including multicolor PSF (3D + color), multi-channel four-dimensional 4Pi-PSF (3D + interference phase) and five-dimensional vortex PSF (3D + dipole orientation). 
Published:
Resolution of single molecule localization microscopy (SMLM) depends on the localization accuracy, which can be improved by utilizing engineered point spread functions (PSF) with delicate shapes. However, the intrinsic pixelation effect of the detector sensor will deteriorate PSFs under different sampling rates. The influence of the pixelation effect to the achieved 3D localization accuracy for different PSF shapes under different signal to background ratio (SBR) and pixel dependent readout noise has not been investigated in detail so far. In this work, we proposed a framework to characterize the 3D localization accuracy of pixelated PSF at different sampling rates. Four different PSFs (astigmatic PSF, double helix (DH) PSF, Tetrapod PSF and 4Pi PSF) were evaluated and the pixel size with optimal 3D localization performance were derived. This work provides a theoretical guide for the optimal design of sampling rate for 3D super resolution imaging.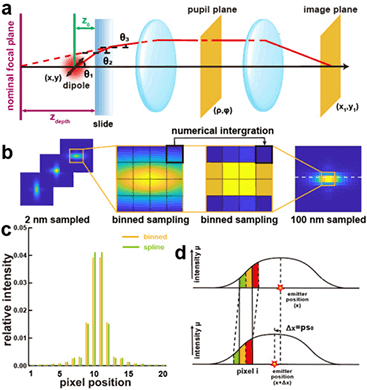
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Published:
Published:
Published:
I am a cell biologist with extensive scientific knowledge in microbiology, host-pathogen interaction and advanced microscopy approaches. I have over 10 years experience in scientific project design/management, undergraduate and postgraduate student supervision and writing/communication of scientific information to both expert and non-expert audiences. To attest to this I am lead author in several high profile publications with over 1300 citations (Google Scholar: dQvQ0AAAAJ), have supervised multiple Master and PhD students, and have been actively involved in several outreach initiatives (In2Science, ITQB-NOVA open day). I have served in several decision boards in Universidade Nova de Lisboa, University College London and the Francis Crick Institute where I have worked with academic, industrial and political partners to define scientific and institutional vision and impact strategies. Experience that has provided me with a comprehensive view about the scientific landscape. From a research point of view I have made significant contributions in the fields of S. aureus microbiology (e.g. discovering a link between peptidoglycan and wall teichoic acids biosynthesis), host-pathogen interaction (e.g. importance of autolysins for immune evasion, or the role of septins in the recognition of intracellular pathogens) and hardware and software technological innovations for microscopy (e.g. NanoJ-Fluidics and NanoJ-SRRF).